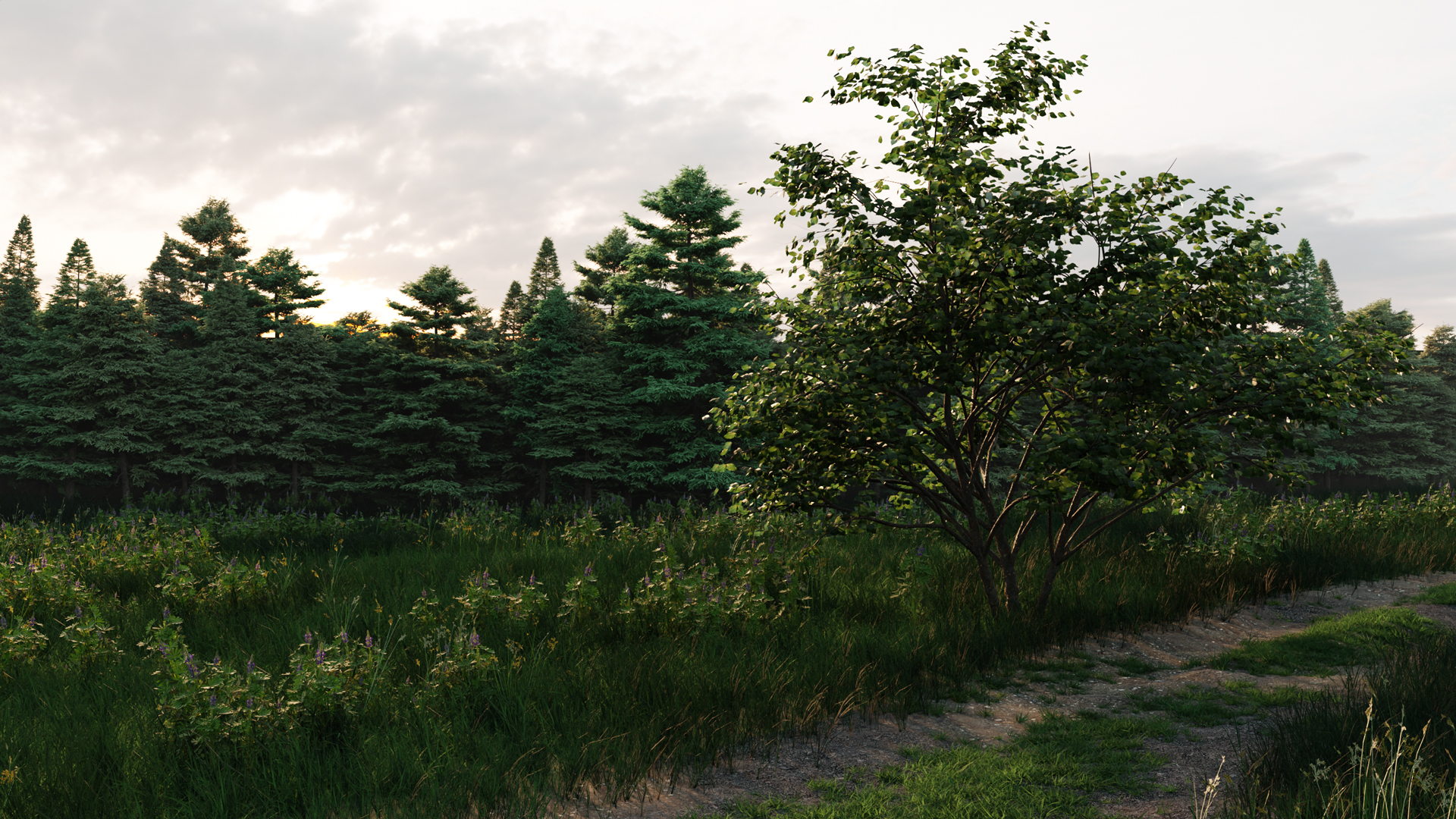
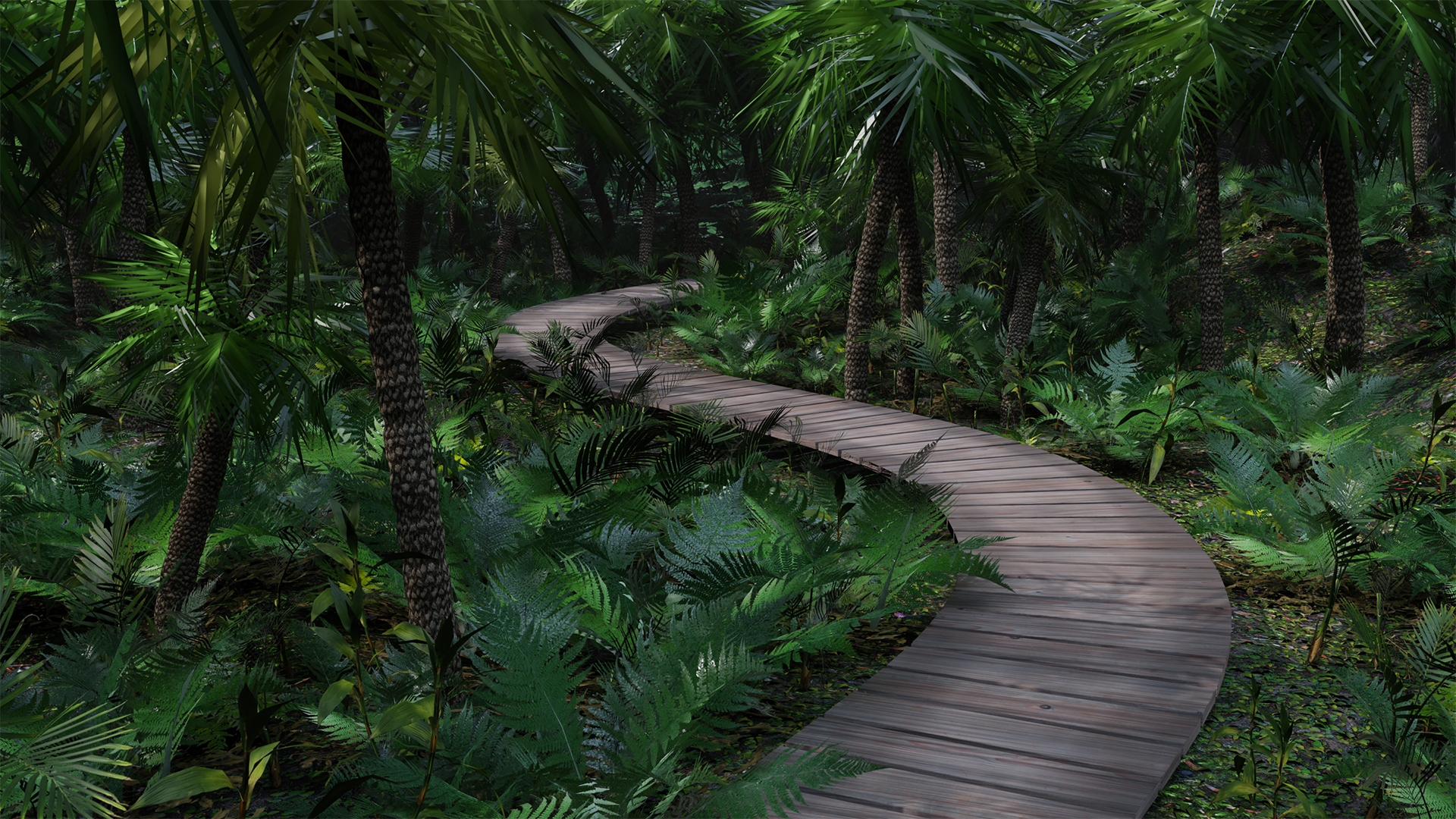
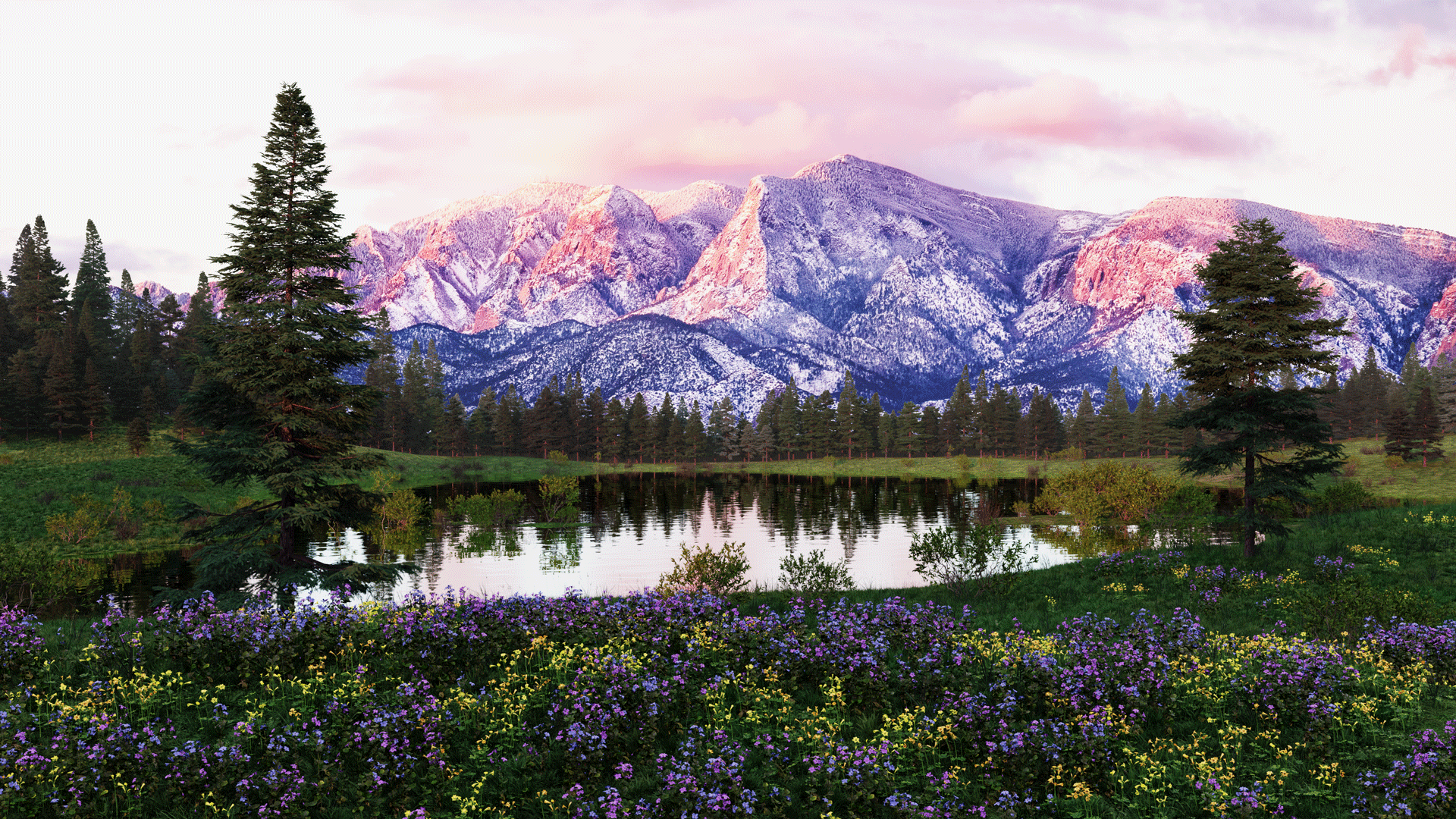
Simple Scatter
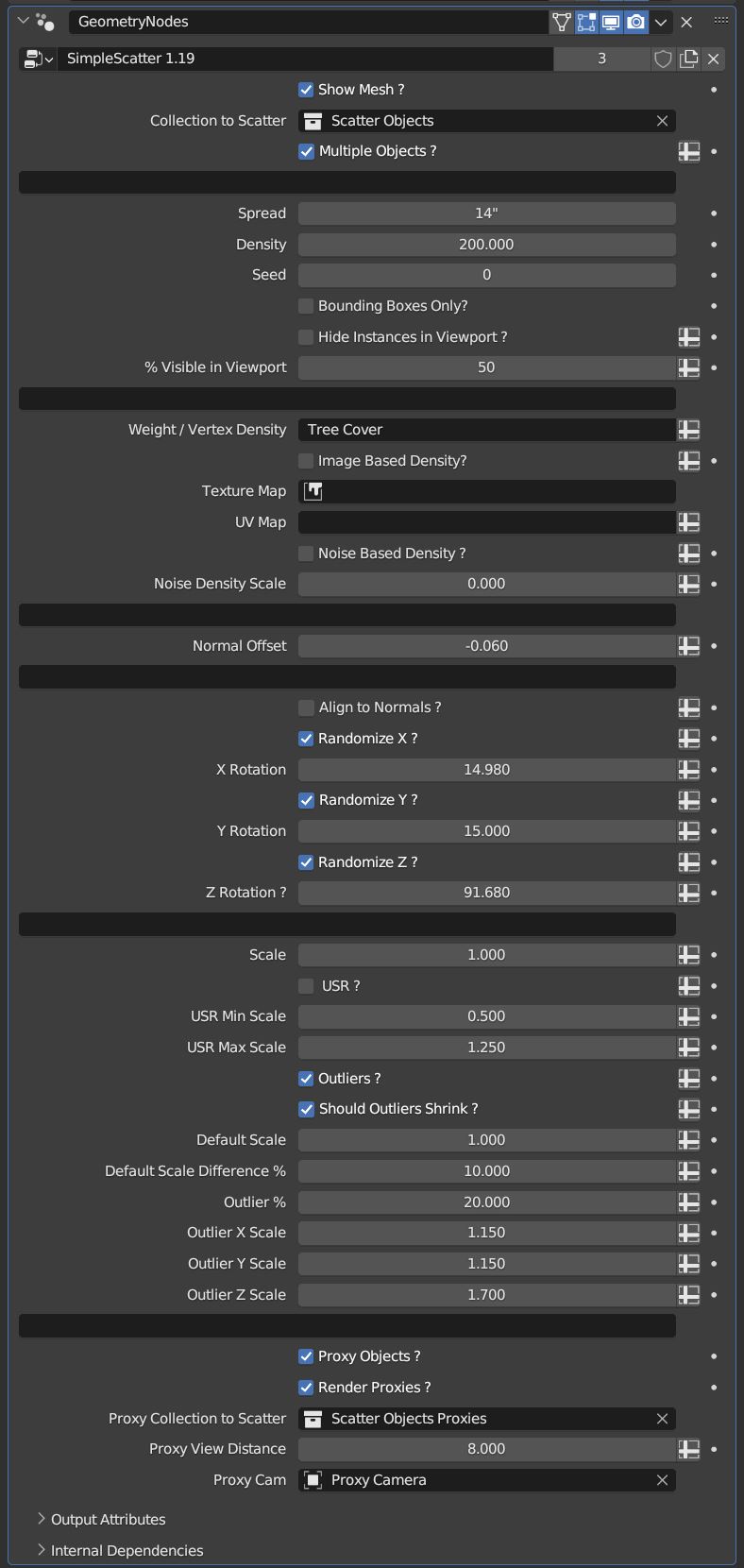
Simple Scatter 1.19
Read Me Guide
This serves as a basic guide to how Simple Scatter functions. It will outline uses and intent of the geometry node setup.
General Notes
· Most fields with the little Attribute Flag and can use weight maps. Just click the flag icon and search for the name of your weight map.
· USR refers to a Uniform Scale Randomizer. This is if you want the scale of an object to remain uniform but want varying sizes of the object.
General Practice
· Density should always be set very low when first using to avoid freezing or system overload.
· Every random rotation function has seed value, not exposed in the interface. You can manually change the rotation seed if you would like by entering the “Rotation Controls” node group.
Inputs
Show Mesh ?
Toggles the mesh the randomizer is applied to.
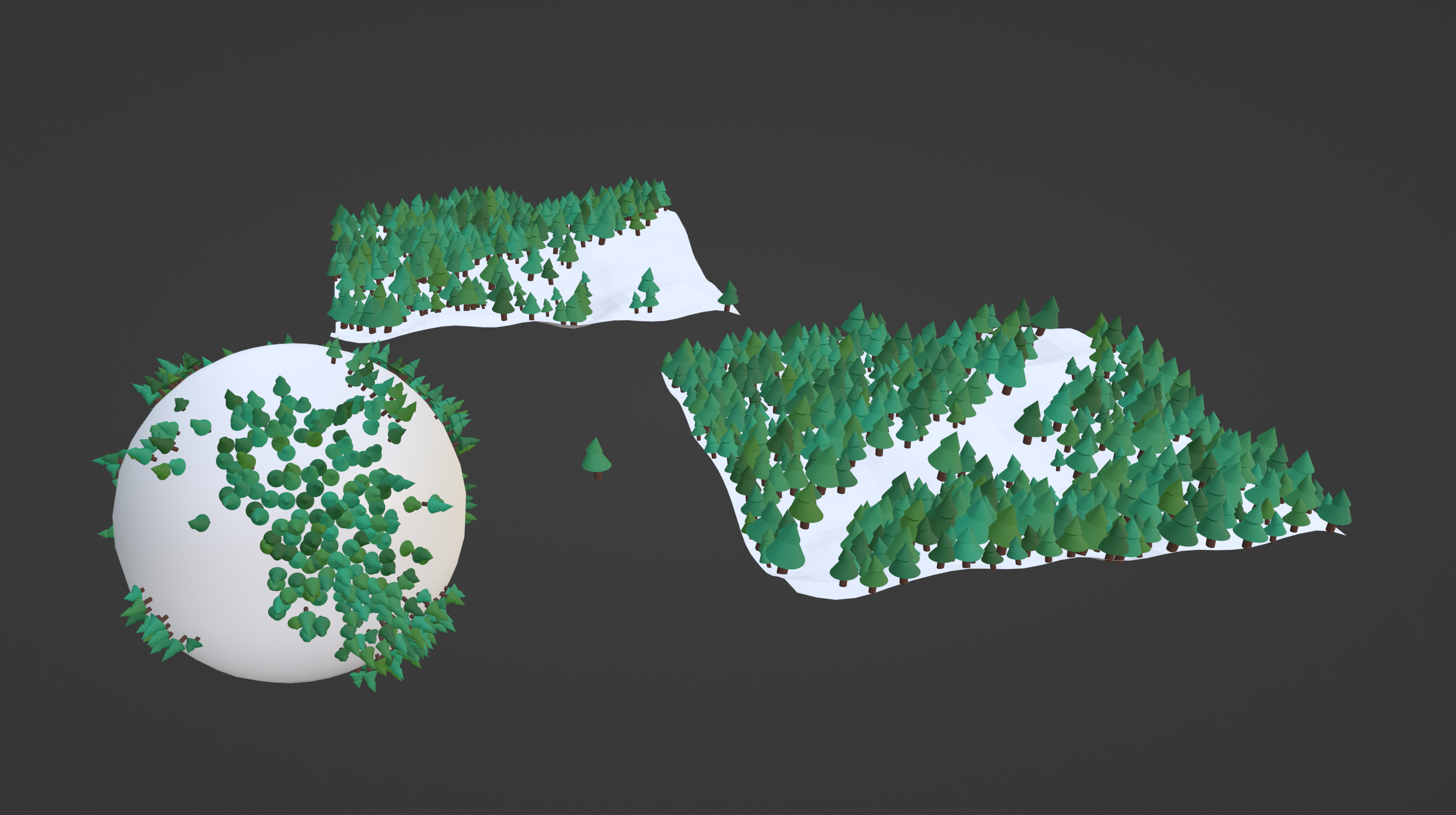
Collection to Scatter
Select a collection of a single item, or a collection of multiple objects to instance.
Multiple Objects ?
Does the collection contain items you want it to separate when instancing?
(Note: Say you have 3 items to scatter, a rock, tuft of grass, and a tree made of several different meshes. Simple scatter may separate the tree and instance the leaves in once place, and trunks without leaves in others. To fix, simply put the tree inside its own collection within the parent collection.)
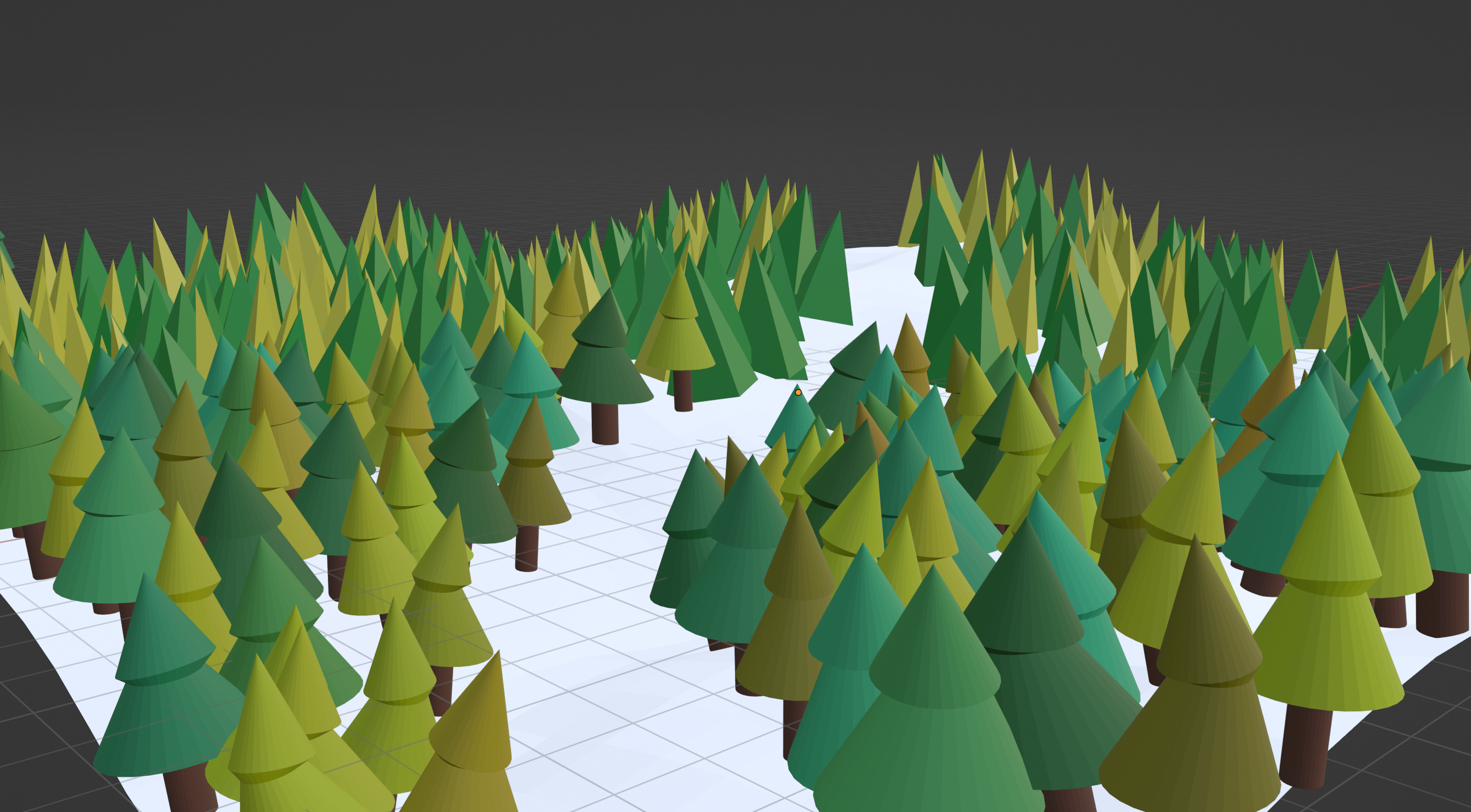
Spread
How far apart can the instances spawn next to one another.
Density
How many objects should spawn on the mesh. If you keep raising the density and aren’t getting more instances, ensure that the spread value is correct. A higher spread will prevent more objects from spawning on a mesh.
Seed
This changes the instances placement on the mesh.
Bounding Boxes ?
This replaces all the objects with simple bounding boxes. Great to visualize densities of high poly objects in a scene.
Hide instances in Viewport ?
Hide the instances spawned, but only in the viewport. They will still render.
% Visible in Viewport
What percentage of instances should be displayed in the viewport. (100% will render, this only alters what is visible in the viewport.)
Density / Weight Options
The system is set up as a waterfall Boolean. It will always default to Weight / Vertex Groups. To use an image texture make sure the ‘Image Texture’ Boolean is set to 1. Doing so will now ignore the weight / vertex group inputs. If you wish to use noise, make sure both the ‘Image Texture ?’ Boolean, and the ‘Noise Based Texture’ Booleans are set to 1. (If the Noise Bool is set to 1, but the Image Bool is set to 0 it will default to the Weight / Vertex system)
Weight / Vertex Group
Initially shown as a value, 0 = 0% and 1 = 100% of the objects are spawned to the mesh. (A more useful option is to click the Attribute Flag symbol and chose a weight / vertex paint map.)
Image Texture ?
Would you like to use an image texture? (Be sure to select you UV Map by clicking the Attribute Flag and searching for it.
Texture Map
Search for the Image you wish to use as your density / weight map. (Ensure the object is UV’d correctly)
UV Map
Click the attribute flag next to this option and search for the UV map you wish to use as a density / weight map.
Noise Based Texture ?
Would you like to use a noise generator for object placement? The noise can be edited within the geometry nodes tab. Look for the group named “Edit Noise Here”, select it and press tab. Inside the usual noise options should be displayed.
Noise Scale
Scaling the noise up and down can be done here. More control over the noise can be achieved through geometry node setup.
Align to Normals ?
Determines if instances are spawned perpendicular to the emitter meshes faces. If 0 all instances will face up on the world Z axis.
(Note: If this is true you can no longer get uniform X and Y rotations as each object is rotated and placed according to the mesh’s normals. This prevents uniformity.
Normal Offset
Should instances spawn higher or lower on the Z axis?
Randomize X ?
Should instances spawn with random X rotations?
X Rotation
Arbitrary numerical value that affects the rotation of each instance.
Randomize Y ?
Should instances spawn with random Y rotations?
Y Rotation
Arbitrary numerical value that affects the rotation of each instance.
Randomize Z ?
Should objects spawn with random Z rotations?
Z Rotation
Arbitrary numerical value that affects the rotation of each instance.
(Note: This node setup will always rotate along the Z axis of the instances local space. You can disable this in the ‘Rotate Instances’ node found in the node setup.
Scale
What scale should the instances spawn at?
USR ? (Will override Non-Uniform Scaling if enabled.)
Should instances have varying, but uniform sizes when spawning?
USR Min Scale
What is the minimum scale an object should be instanced at?
USR Max Scale
What is the maximum scale an object should be instanced at?
Outliers ? (Will not function if USR is enabled.)
This option allows you to still have a variation in size, but then to also have some outliers that can be significantly larger and smaller than the others to break up the uniformity.
Should Outliers Shrink ?
Do you want the outliers to be smaller as well? Turn off if you only want larger outliers.
Default Scale
What is the Default scale of your Instances?
Default Scale Difference %
What is the scale difference between instances? 20% Means object can be up to 120% of the default scale, but can also be 80% of default scale.
Outlier %
How many instances should be Outliers?
Outlier X Scale
How large can instances scale up to on the X axis.
Outlier Y Scale
How large can instances scale up to on the Y axis.
Outlier Z Scale
How large can instances scale up to on the Z axis.
Proxies
Proxy Objects ?
Would you like to use proxies for this project ?
Render Proxies ?
Would you like Blender to render the proxies? Or just use them in the viewport?
Proxy Collection to Scatter
Select the collection containing your proxies. (Note: The order of objects in the collection is important. The Collection to Scatter and the Proxy Collection must maintain the same order.)
Proxy View Distance
The distance, from a camera, that Instances will display their Proxy Geometry in the viewport.
Proxy Cam
The camera that the ‘Proxy View Distance’ will measure from.
(This could also be an object or empty that you can use to move around the scene to see the geometry you want.)
If you have any issues please email me at: simplescatter@gmail.com
Thanks for reading!
Discover more products like this
plants multiscatter instancer #nature grass geometry nodes bfcm23 3d scatter Trees winter24 object scatter environment GEO-SCATTER